Training a chatbot is about more than just feeding it data. It's a process of defining its purpose, giving it high-quality company knowledge from sources like your help docs and FAQs, and then using an AI platform to turn that information into natural conversation. From there, you'll refine its personality with specific prompts, test it relentlessly with real-world questions, and finally deploy it on your website to start delivering instant, on-brand answers 24/7.
Defining Your Chatbot’s Purpose and Personality

Before you upload a single file, the most critical step is to give your chatbot a clear mission. This is where so many projects go wrong. Trying to build an all-knowing AI that can "do everything" is a surefire way to create a tool that does nothing particularly well.
A focused bot that excels at one specific job is infinitely more valuable than a generalist that fumbles through many. The aim here is to build a genuinely helpful assistant, not another source of frustration for your customers.
Set a Primary Goal
First things first: what is the single most important problem you need this bot to solve? A sharp, clear objective will guide every decision that follows, from the content you choose to the personality you craft. Are you trying to free up your support team, or are you looking to engage potential customers when everyone’s gone home for the day?
Here are some common, effective goals I've seen teams succeed with:
- Slash support ticket volume by instantly answering the top 20-30 most common questions.
- Capture qualified leads by engaging visitors on key pages, like your pricing or product tour.
- Streamline internal onboarding by giving new hires a central spot to ask about company policies.
- Provide 24/7 sales assistance by answering detailed product questions when your sales team is offline.
Key Takeaway: Don't just build a "company chatbot." Instead, build a "return policy expert" or a "new-hire onboarding guide." Giving your bot a specific job makes training 10x more effective because you can feed it a curated, hyper-relevant knowledge base.
Craft a Distinct Personality
Once you know what your chatbot is for, you need to decide who it is. The personality should feel like a natural extension of your brand and fit the context of the conversation. For example, an internal IT helpdesk bot can be direct and professional, while a bot on your main website should probably be more friendly and approachable.
This isn't just a fun branding exercise; it directly influences the tone and style of every single answer. The best way to nail this down is to simply write down a few key adjectives. Is your bot:
- Helpful and Professional?
- Friendly and Casual?
- Witty and Engaging?
- Direct and Concise?
Think of this simple definition as a style guide for your AI. It ensures your chatbot feels like a genuine part of your team, which is crucial for building trust and making every interaction a positive one.
Sourcing and Preparing Your Training Data
The single most important factor in your chatbot's success is the quality of the information you feed it. Think about it: you wouldn't hand a new employee a stack of messy, outdated, and contradictory manuals and expect them to perform well. It’s the same with an AI.
The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" has never been more true. A bot trained on junk data will confidently spout nonsense, which is a fast way to lose customer trust. Your job here is to build a clean, curated library of truth—not a digital junk drawer.
Finding Your Best Content Sources
Let's start by gathering the documents your team already uses every day. The best training data is almost always the content you've already created to help people. You're looking for things that are structured, factual, and directly answer the kinds of questions your customers or employees are actually asking.
Good places to start digging include:
- Public-facing content: This is usually your gold mine and the safest place to begin.
- Help center articles and your knowledge base
- Detailed FAQ pages
- Product spec sheets and user manuals
- Official company policies (think shipping, returns, privacy)
- Internal documents: Perfect for a bot that will help your own team.
- Employee handbooks and onboarding guides
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- Internal IT support wikis
This whole process really puts the scale of modern AI into perspective. Training a good chatbot requires a solid dataset, mirroring a trend that saw the global market jump from $2.47 billion in 2021 to a projected $15.57 billion by 2025. While the base models are trained on huge amounts of general web data, it’s your specific, high-quality documents that make a bot genuinely useful for your business. You can dive deeper into chatbot statistics to get the full picture.
To help you decide where to focus your efforts first, let's look at the pros and cons of different content sources.
Content Source Pros and Cons for Chatbot Training
| Content Source | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Help Center/KB | Already structured for Q&A. Usually up-to-date and customer-focused. | Can have gaps if you haven't documented everything. May contain overly technical jargon. |
| Website Pages | Great for general company info, product features, and marketing language. | Often contains marketing fluff that isn't helpful for direct answers. Can become outdated quickly. |
| PDFs (Manuals, Guides) | Contains deep, detailed product information and step-by-step instructions. | Often long and poorly structured for AI. Needs to be broken down into smaller, digestible chunks. |
| Internal Documents | Highly specific to your company's processes. Excellent for internal-facing bots. | May contain sensitive information. Often less polished and can have conflicting versions. |
| Spreadsheets (CSVs) | Perfect for structured data like pricing, product specs, or directories. | Requires clean formatting and clear headers. Useless without context. |
Ultimately, a mix of these sources will give you the most well-rounded chatbot. Start with your help center, then layer in other relevant materials.
The Non-Negotiable Step: Data Cleaning
Once you’ve rounded up your source files, the real work begins. Cleaning your data is so much more than a quick spell-check. It's a strategic audit to root out anything that's inaccurate, inconsistent, or just plain old. An outdated pricing sheet or last year's return policy can cause serious headaches if they sneak into your training set.
My rule of thumb: If a piece of information would confuse a new hire, it will absolutely confuse your chatbot. Ambiguity is the enemy. Your goal should always be crystal-clear information.
Before you upload a single file, give everything a thorough review. Hunt for conflicts between documents—like a product manual that says one thing and a marketing page that says another. Ditch any expired promotional details or old seasonal content. That "Holiday Shipping Deadlines" page from last year? Get rid of it.
Finally, think about structure. A massive, 50-page PDF is tough for an AI to parse effectively. You’ll get much better results by breaking it down into smaller, topic-focused documents. Splitting that huge manual into individual chapters or sections helps the AI pinpoint precise answers, turning your chatbot into a genuinely reliable expert.
Mastering the Core Training Process
Alright, you've gathered and cleaned up your data. Now for the fun part: actually training the chatbot. This is where all that raw information gets molded into a smart, responsive assistant that genuinely helps your users. It really boils down to getting two things right: the system prompt and the training examples.
Think of the system prompt as your chatbot's core programming or its "constitution." It's a foundational set of instructions that dictates its personality, its rules of engagement, and what it should do when it gets stumped. A well-crafted prompt is the anchor that keeps the AI true to its purpose.
Before we dive into writing prompts, it's helpful to visualize the data journey up to this point. You're taking scattered information, cleaning it up, and giving it a clear structure.
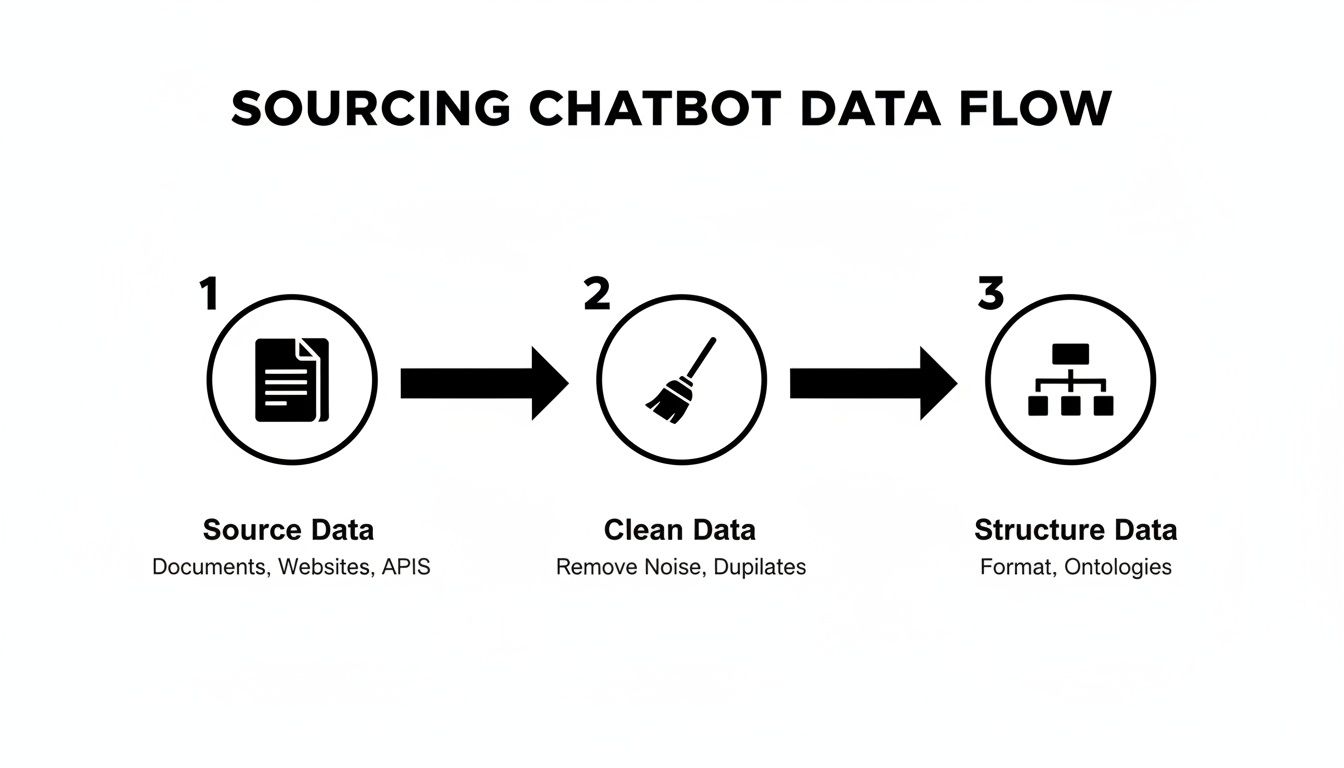
This workflow ensures everything you feed the bot is reliable and ready for training, which is crucial for getting accurate results.
Writing a Powerful System Prompt
The system prompt is where you define the bot's persona and set its operational boundaries. This isn’t a time for subtlety—you need to be incredibly explicit. Don't just tell it to "be helpful." Define what helpful looks like for your company.
For example, a system prompt for a support bot shouldn’t be a vague suggestion. It should be a clear directive:
- "You are a friendly and professional support agent for the company 'BizSage'."
- "Your one and only job is to answer questions using the knowledge base I've provided."
- "If you can't find an answer, you must respond with: 'I'm not sure about that, but I can connect you with our support team for more help.'"
- "Never invent answers or speculate on topics outside of your documentation."
These kinds of direct commands are what prevent a chatbot from "hallucinating" or making things up, which is a real risk with powerful language models. Your prompt acts as the guardrails, keeping every conversation on-brand and factually accurate.
Understanding the broader principles of AI software development can also give you a better appreciation for how these complex systems are engineered from the ground up.
Creating Effective Training Examples
If the system prompt sets the rules, your training examples teach the bot how to actually play the game. These are typically question-and-answer pairs that show the bot what a good response looks like in practice. This goes way beyond just uploading your FAQ page; it’s about anticipating how real people talk and think.
A solid set of training examples will cover a few key areas:
- The Obvious Stuff: Start with the top 20-30 questions your support team gets every single day.
- Different Phrasings: Think about all the ways someone might ask the same question. "What's the return policy?" is one way, but so is "How do I send something back?" or "I need to return this."
- The Weird Questions: Include some edge cases and more obscure queries to test the boundaries of the bot's knowledge.
- Figuring Out Intent: Train it on questions where the user's need is implied, not stated. "My order arrived broken" doesn't ask a question, but it clearly signals a need for the returns and damages policy.
This whole approach is a huge leap from the old, clunky, rule-based chatbots. The big shift happened around 2017 with the invention of transformer architectures, which is the tech that allows a bot to understand context and nuance. It's what has turned chatbots into a scalable tool, with some market segments expected to hit $15.5 billion by 2030. Today, we're not coding rules; we're fine-tuning these powerful models with our specific company data.
Pro Tip: Don't feel like you need to create hundreds of examples on day one. Start with the most critical and frequent questions. The real magic happens after you launch—you can (and absolutely should) keep adding new training examples based on the real questions your bot gets from users.
Testing and Refining Your Chatbot for Real-World Accuracy
So, you’ve loaded your chatbot with all your company’s documents. You’re done, right? Not even close.
Training a chatbot is not a "set it and forget it" task. The real work begins after you’ve fed it the initial data. Before you unleash your new AI on actual customers, you have to put it through its paces to see how it handles the beautiful, messy, and unpredictable nature of human conversation.
Think of this phase less like a final exam and more like a series of intense sparring sessions. The goal is to find the cracks in its knowledge and logic before your users do.
Get Into Your Customer's Head
The best way to kick this off is with a bit of role-playing. Put yourself in the shoes of different customers—the curious, the confused, the frustrated. Don't just lob the clean, perfect questions from your training examples. Try to break it.
Here are a few personas I always use when testing a new bot:
- The Vague Inquirer: This person asks really broad, open-ended questions like, "tell me about your stuff" or "is your service any good?" You're testing the bot's ability to give a solid, helpful summary instead of just freezing up.
- The Frustrated Customer: Use language that signals impatience or a problem. Something like, "this thing isn't working" or "I'm not happy with my purchase." You want to see if the bot can pick up on the negative tone and respond with empathy, pointing them to the right support doc or return policy.
- The Typo King: This one’s my favorite. Intentionally mash the keyboard. Ask questions like "wats ur return polisy?" to see if the language model is smart enough to decipher the intent behind the messy typing.
This isn’t just about finding flaws; it’s about understanding how your training actually translates into a real conversation. The insights you get here are pure gold for the next round of improvements.
Hunt Down Inaccuracies and Hallucinations
Beyond just understanding what a user wants, you have to be relentless about factual accuracy. This is where you actively try to trip up the bot, a technique known as adversarial testing. You're intentionally pushing it outside the boundaries of what it's supposed to know.
Ask it about things you know aren't in the training data. If you’re a marketing agency, ask about your competitor's pricing. If you sell software, ask about a feature you don't offer. What does it do? Does it correctly say, "I don't have that information," or does it completely make something up? That invention is what we call a "hallucination."
A chatbot that confidently spits out wrong information is infinitely more damaging to your brand's trust than one that simply says, "I'm not sure about that, but our human team can help."
Every time you find a failure—a factual error, a weird personality quirk, or just a confusing answer—you’ve struck gold. Each mistake shines a spotlight on a specific gap in your training data or prompts.
Use this feedback to go back and refine your source documents, tweak your bot’s behavioral instructions, or add a new Q&A example to fill that knowledge gap. This constant loop of testing and refining is what elevates a chatbot from a fun gimmick to a genuinely useful tool.
Getting Your Chatbot Live and Keeping It Sharp
After all the planning and testing, it’s finally time to introduce your chatbot to the world. But going live is more than just flipping a switch. It's about strategically placing your new assistant where it can do the most good and setting up a routine to ensure it gets smarter over time.
Think of the launch as day one of its real training. Every single interaction from here on out is a priceless learning opportunity.
How to Get Your Chatbot on Your Site
The good news is that getting your chatbot live is usually the easiest part. Most platforms make it a simple copy-and-paste job, giving you a few straightforward options that don’t require a developer.
You can put your chatbot in a few key places:
- As a website widget: This is the most common approach. A friendly little bubble sits in the corner of your site, ready to pop open when a user needs help without getting in their way.
- On a dedicated landing page: You could create a specific URL, like
support.yourcompany.com, where users can go for a more focused, in-depth conversation. This is perfect for complex support bots. - Embedded directly on a page: Why not put the chatbot right on your pricing or contact page? This offers instant, contextual help exactly when users are making key decisions.
My Two Cents: Don't be shy about your new chatbot. Make it obvious that it's the fastest way for visitors to get answers. A great bot can't help anyone if they don't know it's there.
Setting Up a Monitoring Routine
Once your bot is live, you can't just set it and forget it. The real magic happens when you create a feedback loop to catch its mistakes and capitalize on what it's learning.
This means regularly checking in on its performance. For a small team, a weekly review is a great place to start. Block out an hour to dig into the conversation logs. What you're looking for are patterns—the same questions it can't answer, topics where it gets confused, or moments where users get frustrated.
These are your gold mines. They tell you exactly what new content to add or which training examples need a little tweaking. You're not just fixing errors; you're actively making the bot a more valuable asset. For a deeper dive, read up on implementing AI observability and monitoring to get a handle on the technical side of things.
This isn’t just busywork—it’s where the real ROI comes from. Some companies see returns of 148-200% from well-managed chatbots. And with predictions that 95% of customer interactions will involve AI by 2025, a bot that constantly improves isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a serious competitive edge.
Common Questions About Training a Chatbot
Even with a solid plan, a few questions always come up when you start training a chatbot for the first time. Getting good answers to these common hurdles can help you avoid some classic mistakes and build a much better AI assistant right from the start.
Let’s dig into what teams usually ask.
How Often Should I Retrain My Chatbot?
Honestly, there's no magic number here. The best retraining schedule is tied directly to how often your company's information changes. Think of it as linking your bot's updates to your own content calendar.
For a customer support bot dealing with ever-changing product features, you’ll probably want to refresh its knowledge base monthly or quarterly. But if you're building an internal bot that just knows the employee handbook—which rarely changes—a quick update once or twice a year is likely plenty.
The real secret? Let your users tell you when it's time. If you start seeing a bunch of "I don't know" responses or notice people asking about a new product you just launched, that's your signal. It's time to add the new content and hit sync.
What Is the Biggest Mistake to Avoid?
The single worst thing you can do is rush the process and feed your bot "dirty" data. I know how tempting it is to just upload a massive folder of every document you have and hope for the best, but that approach almost always leads to disaster.
When you do that, you end up with a chatbot that confidently gives answers that are outdated, conflicting, or just flat-out wrong. The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" is the first rule of AI. A small, carefully curated set of documents will always beat a huge, messy one. Taking the time to clean up, update, and organize your source content is the single best investment you can make in your bot's success.
Can I Train a Chatbot to Have a Specific Personality?
Absolutely! And you really should. A chatbot’s personality is shaped by its system prompt—the foundational instructions you give the AI. This is where you get to define its character and tone with incredible detail.
For instance, you can tell it to be:
- Friendly and professional: "You are a helpful support agent. Your tone is courteous and clear."
- Witty and engaging: "You are a clever brand mascot. Feel free to use puns and clever wordplay."
- Direct and concise: "Get straight to the point. Avoid fluff and keep answers short."
A simple line in your prompt like, "You are an energetic brand expert. Always be encouraging and end your answers with a positive note," can make a huge difference. You can then fine-tune this persona by feeding it training examples that reflect that voice and correcting any off-brand answers you spot during testing. Over time, it will start to feel like a genuine extension of your team.
Ready to turn your company's knowledge into a 24/7 expert? With BizSage, you can train a custom AI chatbot on your website content, documents, and FAQs in minutes—no developers needed. Start deflecting repetitive questions and giving your customers instant, on-brand answers today. Learn more at BizSage.io.
